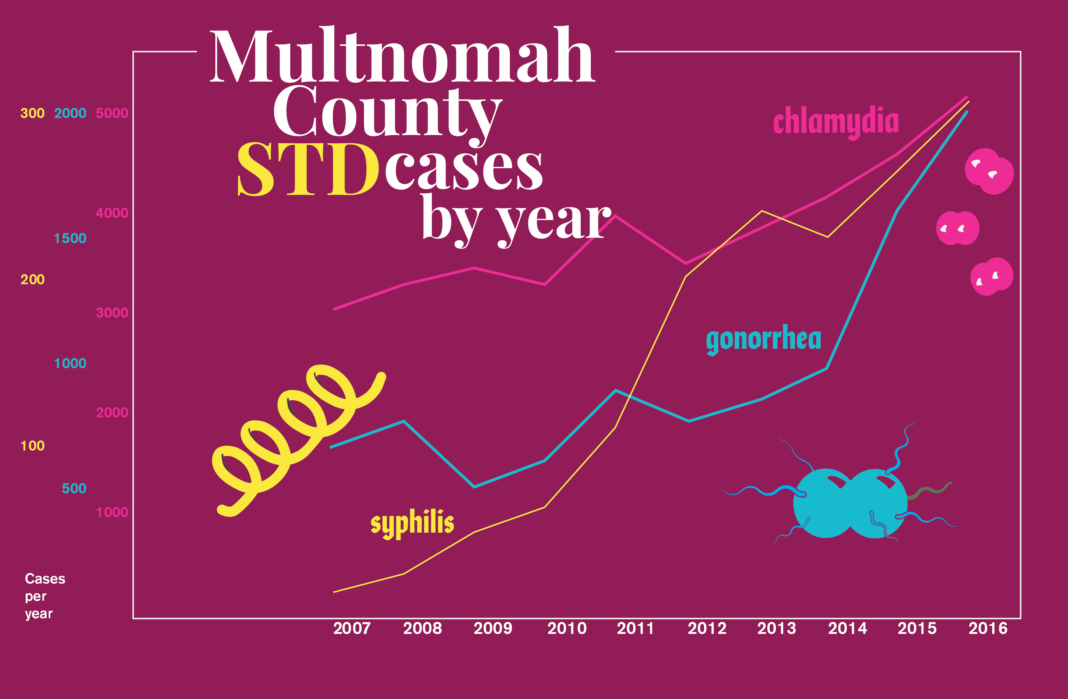
Transmission of STIs continues to be an issue in the United States and in Multnomah County, Ore. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, STDs have been on the upswing in the U.S. As of 2016, the three most common STIs are chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Each of these STIs affect all sexes equally and have the ability to be asymptomatic.
Chlamydia
Regardless of your sex, symptoms of chlamydia include abnormal discharge and burning sensations during urination. When chlamydia infects the rectum, pain, discharge and bleeding may occur. Chlamydia can cause pain and swelling in one or both testicles. Untreated chlamydia can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, causing infertility and complications for pregnancy later on.
Gonorrhea
Universal symptoms of gonorrhea are painful urination, increased or abnormal discharge or irregular bleeding from genitals or rectum. Females often experience symptoms similar to a common bladder infection. Gonorrhea can cause pain and swelling in one or both testicles. Neglecting treatment can also cause infertility in all individuals.
Syphilis
Syphilis develops over three disease stages: primary, secondary and tertiary. This STD can also enter a latent stage in which symptoms are undetectable. The disease can easily develop from secondary to tertiary stage, carrying dangerous health implications with it.
Primary syphilis symptoms usually involve sores at the infection site. The sores are typically firm, round and painless and can take up to six weeks to heal. Although the sores heal without treatment, the disease can be treated properly to avoid progressing into secondary stage.
Secondary syphilis symptoms are typically mild and not always noticeable. Symptoms involve a skin rash or skin lesions around mucosal membranes, such as oral tissue or skin in and around the genitals and anus. Swollen lymph nodes are often accompanied with a fever, and a rough, dry spotted rash will appear on the palms of hands and feet.
Tertiary stage is the most dangerous stage of syphilis, as it usually develops over a latent period of 10–30 years. The patient may be completely unaware of their disease. Severe medical problems can affect important body organs such as the heart, brain and eyes. Neurosyphilis and ocular syphilis result from tertiary stage and may also be associated with symptoms such as patchy hair loss, sore throat, headache, weight loss, muscle aches and chronic fatigue.
Each of these STIs are generally most common for individuals between the ages 17–25 and can be transmitted through body fluids, oral sex, vaginal intercourse or anal sex. All three STIs are curable and preventable, but also incredibly contagious. The only way to avoid contracting STIs is through using protection and having regular health checkups with your doctor.